What to Expect with a Dental Bone Graft Procedure
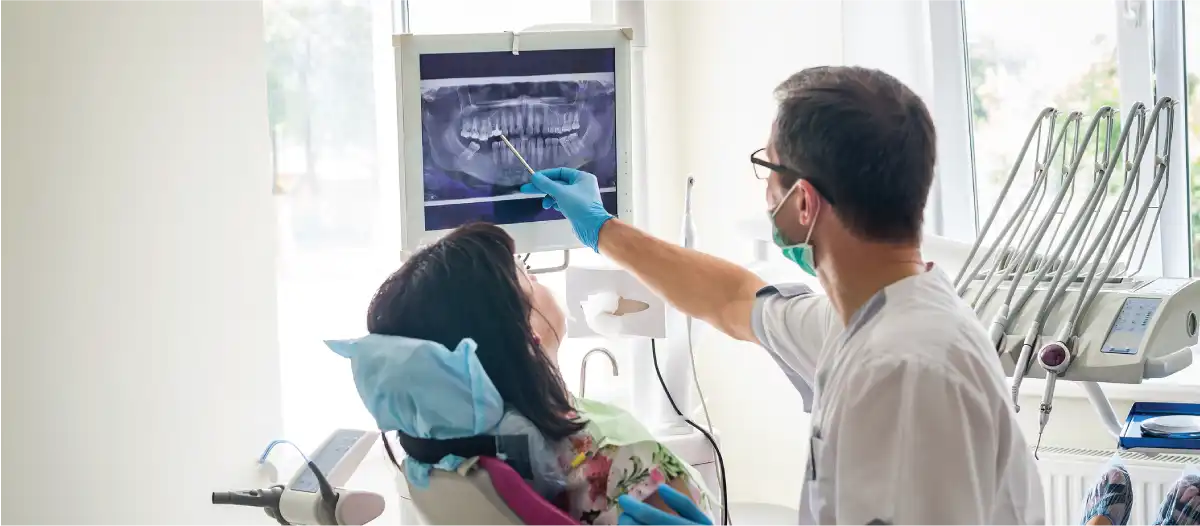
Dentist recommended a bone graft? Your first question may be, “What on Earth is that?”
Bone grafting procedures often serve as a foundational step in supporting various other treatments like implants or dentures. In this article, we’ll dive into how bone grafting works, who may benefit from the treatment, types of bone grafting and factors that affect the cost of the procedure.
What is a bone graft?
A bone graft is a surgical procedure used to repair and rebuild bone that has been damaged or lost due to injury, disease or other conditions. It involves transplanting bone tissue from another part of the body (autograft), from a donor (allograft) or using synthetic materials (alloplastic graft) to stimulate bone regeneration.
How does a bone graft work?
Regardless of what type of bone graft you get, the principle remains the same: to provide a foundation that supports the growth of new bone cells.
During a bone graft procedure, the surgeon begins by making an incision at the site of the graft. If using an autograft, bone tissue is harvested from the donor site. The dentist will move the gum tissue back slightly, then place the graft material and secure it in place with stitches.
The graft material integrates with the surrounding tissue to mimic the bone healing process and stimulate cell production. Over time, the material is replaced by newly formed bone, resulting in a stronger and more stable structure.
Who needs a dental bone graft?
A bone graft may be recommended for individuals who have experienced bone loss in their jaw due to various factors, like:
- Tooth loss: When a tooth falls out or is extracted, the surrounding bone may begin to deteriorate over time due to lack of stimulation from chewing. A bone graft rebuilds the bone volume in preparation for dental implants or to provide support for dentures or bridges.
- Periodontal disease: Advanced periodontal (gum) disease can lead to the destruction of the bone supporting the teeth. In cases where the bone has been significantly compromised, a bone graft may be necessary to restore stability and prevent further tooth loss.
- Trauma or injury: Traumatic injuries to the face or jaw can result in bone fractures or loss of bone tissue. A bone graft may be performed to repair the damaged bone and restore normal function and appearance.
- Congenital defects: Some individuals may be born with abnormalities in the structure of their jawbone. Bone grafts correct these issues and improve overall oral health and function.
Benefits of bone grafting
Bone grafting is a versatile procedure that offers several important benefits for patients undergoing various orthopedic and dental treatments. Here are the key advantages.
Bone regeneration
One of the primary benefits of bone grafting is its ability to stimulate the body’s natural healing process and promote the regeneration of new bone tissue. Whether it’s repairing a fracture, filling a bone defect or preparing for dental implant placement, bone grafts provide the essential framework and support for new bone growth.
Improved stability and function
By restoring lost or damaged bone tissue, bone grafting helps improve the stability and use of the affected area. Whether it’s a weakened joint, fractured bone or a compromised dental ridge, bone grafts provide the structural support necessary for speaking and chewing.
Preservation of bone structure
In situations where bone loss has occurred due to injury, disease or aging, bone grafting helps preserve the remaining bone structure and prevent further deterioration. This is particularly important for maintaining facial aesthetics, supporting adjacent teeth and preventing further complications.
Versatility and compatibility
Bone grafting techniques have evolved significantly over the years, offering a wide range of options to suit individual patient needs. The procedure can be tailored to each patient’s unique anatomy and circumstances, ensuring optimal outcomes and compatibility.
Risks of bone grafting
Bone grafting is generally considered a safe and effective procedure. But like any surgical intervention, it carries certain risks and potential complications. It’s important to be aware of these risks and discuss them with your healthcare provider before undergoing bone grafting.
The following are the potential risks associated with the procedure:
- Infection
- Pain and discomfort
- Heavy bleeding
- Graft failure
- Nerve damage
- Allergic reaction
Types of dental bone grafting
There are several types of dental bone grafting techniques tailored to address specific patient needs and circumstances.
- Socket preservation grafts are performed immediately after a tooth extraction to preserve the bone volume and shape of the extraction site. The graft material is placed into the socket left by the extracted tooth, helping to prevent bone loss and maintain the integrity of the jawbone for future dental implant placement.
- Ridge augmentation involves adding bone graft material to a deficient dental ridge to increase its height or width. This procedure is typically recommended when the jawbone has experienced significant resorption or deformities, making it difficult to support dental implants or prosthetic devices.
- Sinus lift (sinus augmentation) is performed in cases where the upper jaw lacks the bone height necessary for dental implant placement. During this procedure, bone graft material is added to the sinus floor to increase the bone height and create a stable foundation for dental implants in the posterior maxilla.
- Block bone grafting involves harvesting a small block of bone from another part of the body, such as the chin or jaw, and securing it to the deficient area using screws or other fixation devices. This is used in cases where a significant amount of bone augmentation is required.
- Guided bone regeneration (GBR) is a technique where the surgeon places a barrier membrane over the bone graft material to protect it and prevent soft tissue growth, allowing the bone to regenerate undisturbed. GBR is usually used in conjunction with other grafting procedures to optimize the outcome of treatment.
- Alveolar distraction osteogenesis is a specialized bone grafting technique that gradually separates and lengthens the bone using a distractor device. This procedure is often used in cases of severe bone deficiency or atrophic ridges to create new bone and enhance bone volume for dental implant placement.
Dental bone graft cost
The cost of a dental bone graft varies depending on several factors, the first being where you receive treatment. Generally, bone grafting is considered a specialized procedure and may incur additional expenses compared to routine dental treatments. You can expect to pay anywhere between several hundred and several thousand dollars.
Other factors include:
- Type of bone graft
- Graft material
- Surgical expertise
It’s also important to note that the cost of a dental bone graft is just one component of the overall treatment plan for restoring oral health and function. Other treatments like tooth extraction, dental implant placement, dentures or periodontal therapy for gum disease may also contribute to the final cost. Plus, ongoing maintenance and follow-up care may also incur additional expenses over time.
Dental insurance can help
In many cases, dental insurance helps to alleviate the financial procedures of bone grafting. While coverage and benefits vary depending on your specific policy, explore your options and inquire about coverage for bone grafting and related treatments.
By using dental insurance benefits, you can access the care you need to restore oral health and function, paving the way for a confident smile and improved quality of life.
